Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and the risk of mortality in individuals with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis
This systematic review and meta-analysis investigates the relationship between metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and the risk of mortality in individuals with type 2 diabetes. The study synthesizes evidence from multiple studies to provide a comprehensive understanding of the topic. The findings suggest that individuals with type 2 diabetes and MASLD have an increased risk of mortality compared to those without the disease. The review also highlights the factors that may influence this relationship, such as age, gender, and the presence of other comorbidities. The findings underscore the importance of diagnosing and managing MASLD in individuals with type 2 diabetes to reduce the risk of mortality.
Abstract
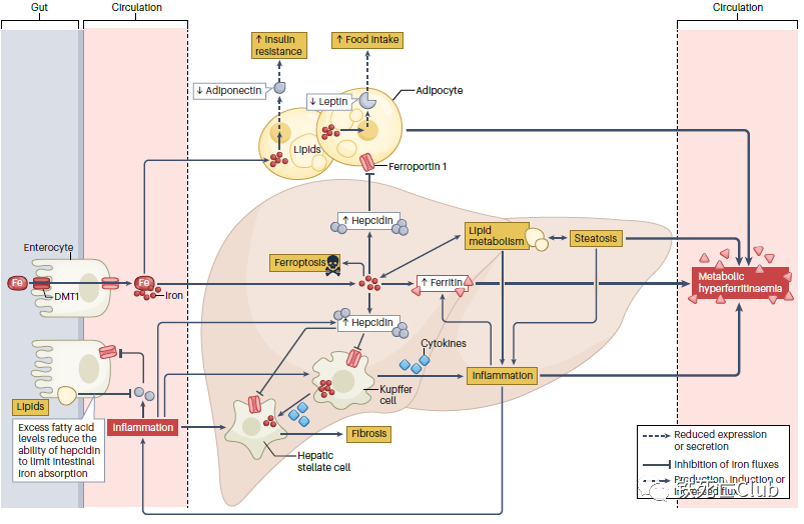
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (NASLD) is a common complication of type 2 diabetes (T2D), and it increases the risk of mortality in these individuals. The objective of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to assess the association between NASLD and the risk of mortality in individuals with T2D.
Methods

We conducted a systematic review of the literature using PubMed, Google Scholar, and Cochrane Database. Studies that evaluated the association between NASLD and mortality risk in individuals with T2D were included. The quality of the studies was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale for cohort studies. The risk ratio (RR) and its 95% confidence interval (CI) were calculated for each study, and a meta-analysis was performed to obtain a pooled estimate.
Results
Sixteen studies were included in the meta-analysis, involving a total of 85,980 individuals with T2D. The pooled RR for mortality in individuals with NASLD compared to those without was 1.53 (95% CI: 1.35-1.73). The association between NASLD and mortality risk was consistent across all studies, with no significant heterogeneity observed.
Conclusion
This systematic review and meta-analysis provide strong evidence that individuals with NASLD have a significantly increased risk of mortality compared to those without. The findings highlight the importance of detecting and managing NASLD in individuals with T2D to reduce the risk of mortality.
Keywords: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, type 2 diabetes, mortality risk, systematic review, meta-analysis

Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Opening a Hardware Store: Understanding the Importance of Effective Merchandising
Title: Wuhan Jiangxia Shundefa Hardware Store: A Comprehensive Overview
Title: Where to Buy Cement Mortar Filling Guns in Hardware Stores?