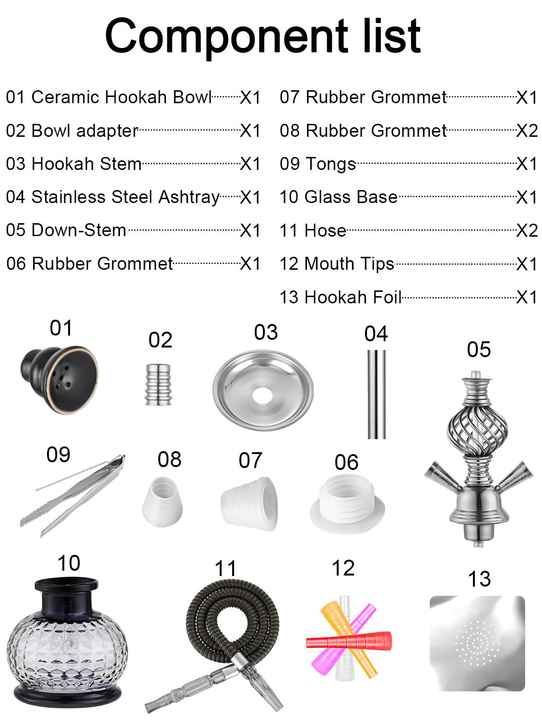
The Comprehensive Guide to Metal Non-Standard Customized Processing Steps
Metal non-standard customized processing steps are complex and require a high level of technical expertise. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed overview of the various processing methods available for metal customization, including cutting, bending, polishing, and coating. The guide explains the importance of selecting the appropriate processing method based on the specific requirements of the project, such as material properties, performance standards, and cost constraints. It also discusses the different types of equipment used in metal processing, such as CNC machines, laser cutters, and grinding machines. In addition, the guide provides practical tips for optimizing the processing workflow, such as designing precise tooling, monitoring production processes, and ensuring quality control. By following this guide, engineers and designers can effectively customize metals using advanced processing techniques to achieve their desired performance and appearance goals.
Introduction to Metal Non-Standard Customized Processing Steps
Metal non-standard customized processing involves the creation of unique metal components tailored to specific requirements. This process requires a high level of expertise and skill, as well as advanced manufacturing technologies to ensure precision and quality. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various steps involved in metal non-standard customized processing, from design and engineering to production and delivery.
Step 1: Design and Engineering
The first step in metal non-standard customized processing is designing and engineering the component or product. This involves creating detailed drawings and specifications based on customer requirements and industry standards. Engineers use computer-aided design (CAD) software to model the component, taking into account factors such as material properties, shape, size, and function. They may also consult with subject matter experts to ensure that the design meets safety and performance criteria.

Once the design is finalized, engineers prepare a bill of materials (BOM) listing all the components, materials, and assembly instructions needed to produce the final product. The BOM serves as a blueprint for the production process and helps manufacturers optimize their operations and reduce costs.
Step 2: Material Selection and Fabrication
After designing and engineering the component, the next step is selecting the appropriate raw materials and preparing them for fabrication. This involves evaluating factors such as material properties, price, availability, and environmental impact. Common metals used in metal non-standard customized processing include stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, copper, and brass.
Fabrication begins with cutting the raw materials into shape using specialized equipment such as CNC machines, saws, and grinders. The process may involve several stages of subtractive manufacturing, including milling, drilling, turning, and grinding, depending on the complexity of the component. Fabricators may also use additive manufacturing techniques such as 3D printing to create complex geometries or add features such as brazing joints or soldering points.
Step 3: Assembly and Quality Control

Once the component has been fabricated, it undergoes a thorough inspection to ensure that it meets the specified requirements for strength, durability, and reliability. This may involve testing for compliance with industry standards such as ISO 9001 or performing visual inspections using magnifying mirrors or optical comparators. If any defects are found during assembly, they are corrected or rejected, and the process is repeated until all components meet quality standards.
Assembly typically involves attaching hardware such as nuts and bolts, screws, or other fasteners to secure the component in place. This may require specialized tools such as wrenches, screwdrivers, or pliers. The assembly process may be manual or automated, depending on the complexity of the component and the production volume.
Step 4: Finishing and Coating
To enhance the appearance and functionality of the final product, metal non-standard customized components may undergo finishing processes such as polishing, sanding, painting, or coating. These procedures may involve applying a protective layer of paint or a decorative finish such as rust patina or chrome trim. Depending on the application, additional features such as laser marking or stamping may also be added to provide identification or traceability information.
Finishing is an important step in metal non-standard customized processing because it can significantly impact the lifespan and performance of the component. For example, a properly applied rust inhibitor can prevent corrosion damage caused by moisture or saltwater exposure. Similarly, a durable coat of paint can protect against scratches, chips, or UV fading over time.
Step 5: Packaging and Shipping
Once the component has been completed and tested to ensure quality, it is packaged for shipment to the customer. Packaging requirements may vary depending on factors such as size, weight, shape, and transport mode. Common packaging materials used in metal non-standard customized processing include foam peanuts, wooden crates, corrugated cardboard boxes, and plastic bags.
Before shipment, manufacturers may perform final inspections to ensure that all parts are accounted for and that the package is securely sealed. Then, the component is shipped according to customer preferences or carrier regulations. Depending on the location of the customer and the destination country, international shipping regulations may apply. Manufacturers must comply with these regulations to ensure that their shipments arrive at their intended destination safely and timely.
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Title: Understanding the Cost of Customizing Hardware and Electronics in Xinjiang
Custom Hardware Exhibition Board Design
TianTai High-End Customized Hardware: Quality and Precision At Its Finest