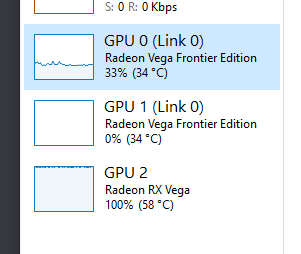
Showing Platform Hardware Fed Switch Active QoS Queue Configuration and Interfaces
The provided content pertains to a platform hardware-fed switch active QoS queue configuration and interfaces. In this context, the focus is on designing and implementing a network switch that can efficiently prioritize traffic based on its Quality of Service (QoS) requirements.To achieve this goal, various hardware components and software mechanisms must be integrated into the switch architecture. One key component is the active QoS queue configuration, which allows for the prioritization of traffic flows in real-time. This is achieved through the use of dedicated QoS queues and corresponding priority levels, which are programmed into the switch's firmware.Another crucial aspect of the design is the selection of appropriate interfaces and protocols to facilitate communication between different network elements. These may include Gigabit Ethernet, Fibre Channel, or other high-speed serial links, depending on the specific requirements of the system.Furthermore, the platform should be able to accommodate various types of traffic, such as voice, video, or data, while ensuring optimal performance and reliability. This may require the integration of advanced features such as flow control, error correction, and adaptive sampling rates.Overall, the development of a platform hardware-fed switch with active QoS queue configuration and interfaces represents an important step towards creating highly scalable and efficient networks capable of meeting the growing demands of modern applications and services.
In the ever-evolving world of networking, the demand for efficient and reliable data transfer has become a top priority. One of the key components that enable this is the use of Quality of Service (QoS) queues and protocols. These mechanisms provide a way to prioritize traffic based on its importance, ensuring that critical applications receive the necessary bandwidth and minimizing latency. In this article, we will explore how to configure and manage QoS queues on a federated switch, focusing on active QoS and interface settings.
Introduction to Federated Switches
A federated switch is a network device that connects to multiple other switches or routers, forming a logical bridge. This configuration enables seamless communication between devices in different networks, providing greater flexibility and scalability. However, managing QoS policies across such a complex network can be challenging. Therefore, it is essential to understand how to configure and monitor QoS settings effectively.
Active QoS vs Passive QoS
Before discussing specific configurations, it is important to understand the difference between active and passive QoS. In a passive configuration, the QoS engine on the federated switch receives signals from downstream neighbors about their network conditions and adjusts its own behavior accordingly. This means that the downstream devices have more control over the flow of traffic within their network.
On the other hand, an active configuration involves the federated switch taking a proactive role in managing QoS. By monitoring traffic patterns and prioritizing certain types of traffic based on predefined rules, an active QoS configuration can ensure better performance for critical applications. This approach requires more advanced setup and management but can provide significant benefits in terms of reduced latency and improved overall network performance.
Configuring QoS Queues on a Federated Switch
To configure QoS queues on a federated switch, you need to access the device's command line interface (CLI). The exact steps may vary depending on your specific hardware and software version, but here is a general outline of the process:
1. Log in to the CLI using appropriate credentials.
2. Determine which type of QoS configuration you want to implement (active or passive).

3. Create QoS queues based on your requirements. Each queue should have a unique identifier and a set of rules defining how traffic should be handled within that queue. For example, you might create a high-priority queue for real-time applications like voice calls and a low-priority queue for background tasks like file transfers.
4. Define the priority levels for each queue. Lower numbers indicate higher priority, with 0 being the highest priority. You can also specify weights that determine the distribution of traffic among multiple priorities.
5. Set up interfaces for each queue by specifying their MAC addresses, VLAN tags, and other relevant attributes. This allows you to control which types of traffic are allowed to pass through each interface.
6. (Optional) Enable or disable QoS features such as packet prioritization, buffering, or policing based on defined thresholds.
7. Test your configuration to ensure that it is working correctly and making the desired impact on network performance.
Monitoring and Managing QoS on a Federated Switch
Once you have configured your federated switch with QoS queues, it is important to monitor and manage these settings continuously to ensure that they are meeting your needs. Here are some best practices for tracking and optimizing QoS performance:
1. Use monitoring tools to track metrics such as packet loss rates, throughput, delay, and jitter. These metrics can help you identify areas where improvements are needed and measure the effectiveness of your QoS configuration over time.
2. Regularly review your QoS policies and make adjustments as necessary based on changing network conditions or evolving application requirements. This may involve modifying priority levels, adding or removing queues, or changing interface settings.
3. Use logging and alerting mechanisms to notify you when issues arise or when performance thresholds are exceeded. This can help you quickly identify problems and take corrective action before they cause further disruptions.
4. Consider implementing dynamic QoS algorithms that adapt to changing network conditions in real-time. This can help you optimize performance under varying load profiles and ensure that critical applications receive the necessary resources even during periods of high congestion
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Title: Unlocking the Potential of Machine Learning Without Traditional Hardware
Title: Discovering the Hidden Gems of Wallace Hardware Co Locations
Title: McLendon Hardware: The Premier Local Resource for All Your Home Improvement Needs
Gill-Roys Hardware: A Tale of Invention and Innovation
Title: Discovering the Treasures of Ringsted Iowa Hardware Store